
Increased urination at night (nocturia) is very common, especially in adults. The phenomenon is also present in women but is especially acute in older men suffering from benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Excessive urination, especially more than twice during the night, impairs sleep quality and can cause sleep disturbances. Doctors' common explanation that the phenomenon is related to the amount of fluid a person drinks, especially before bedtime and even the drinking rate, is too simplistic.
The bladder and kidneys are scheduled to perform self-cleaning in the afternoon.
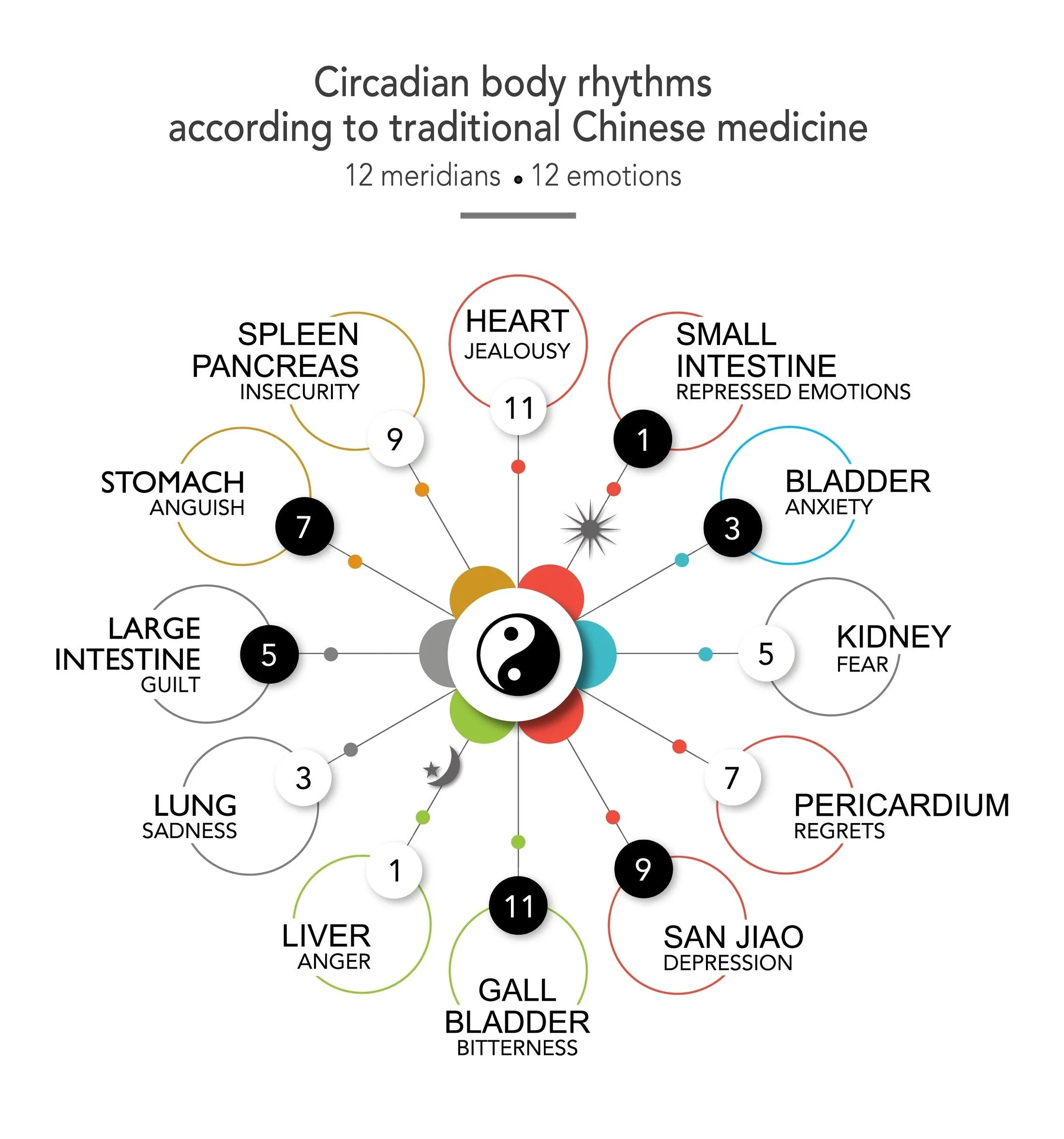
Night urination is mainly related to liver function that affects the kidneys and bladder.
The liver is a painless organ that suffers especially from the modern diet, primarily industrialized and processed. Liver damage, even those not defined as liver disease, such as fatty liver, puts much strain on the liver. Since the liver self-cleanses at night, between 1 and 3 a.m., the cleansing products and acute toxins irritate the bladder and require emptying. The liver and kidneys have complementary metabolic activities; therefore, it is unsurprising that liver cleansing is expressed at night urination.
How to reduce nocturnal urination?
Of course, it is not advisable to drink much before bed, even if you drink a little! The impact will only be marginal. The main effect is associated with an anti-inflammatory diet, complete avoidance of industrialized foods, and regular exercise. As your inflammation decreases, so does the frequency of nighttime urination. In older men who suffer from BPH, more is often needed.
Links:
The balanced-varied diet is the most suitable anti-inflammatory diet.
Chronic Prostatitis, Epididymitis, and BPH.

